Console Manual
Linkis1.0 has added a new Computation Governance Console page, which can provide users with an interactive UI interface for viewing the execution of Linkis tasks, custom parameter configuration, engine health status, resource surplus, etc, and then simplify user development and management efforts.
1. Structure of Computation Governance Console
The Computation Governance Console is mainly composed of the following functional pages:
- Global History
- Resource Management
- Parameter Configuration
- Global Variables
- ECM Management (Only visible to linkis computing management console administrators)
- Microservice Management (Only visible to linkis computing management console administrators)
Global history, resource management, parameter configuration, and global variables are visible to all users, while ECM management and microservice management are only visible to linkis computing management console administrators.
The administrator of the Linkis computing management desk can configure through the following parameters in linkis.properties:
wds.linkis.governance.station.admin=hadoop (multiple administrator usernames are separated by ‘,’)
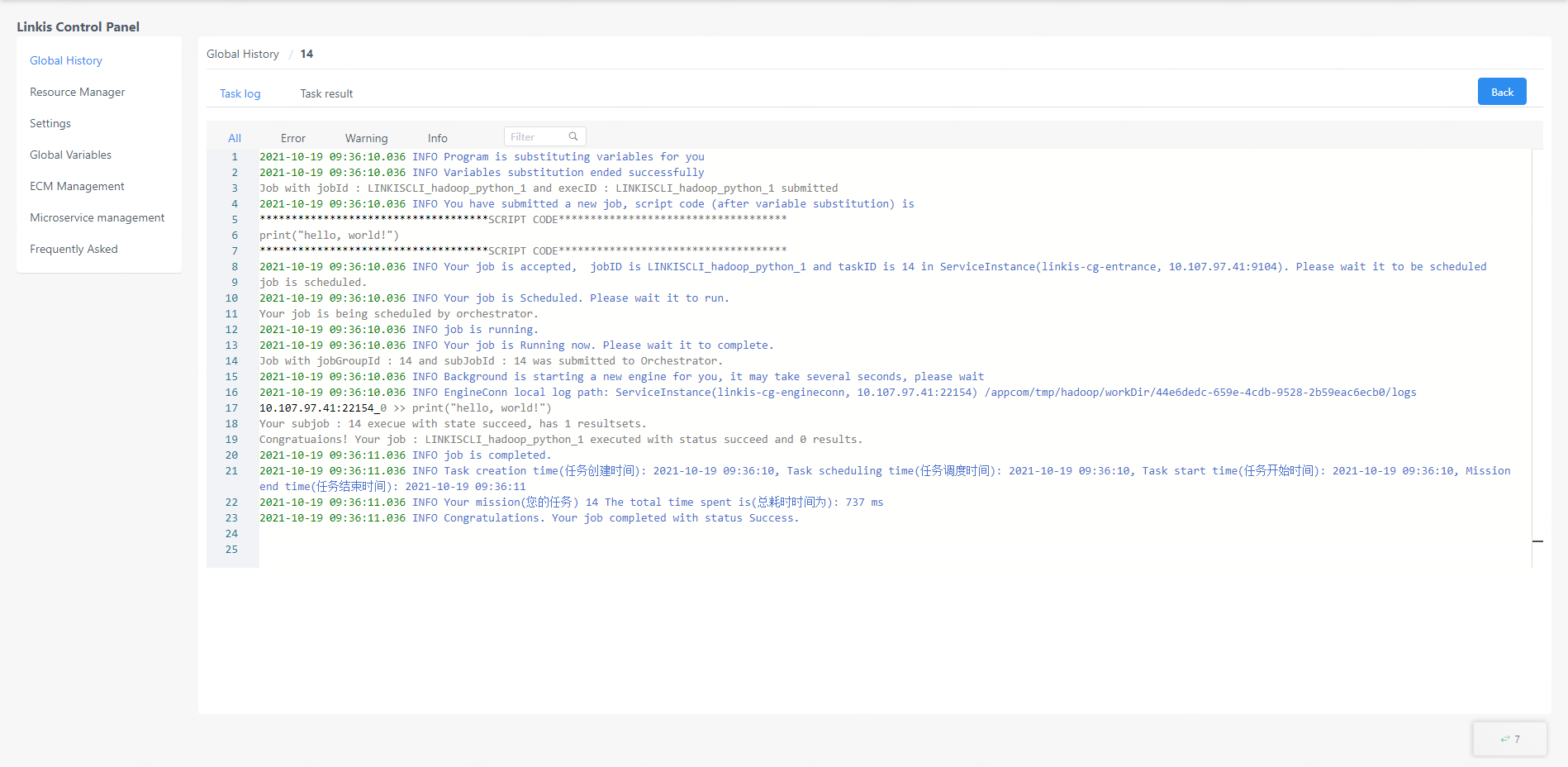
2. Global history
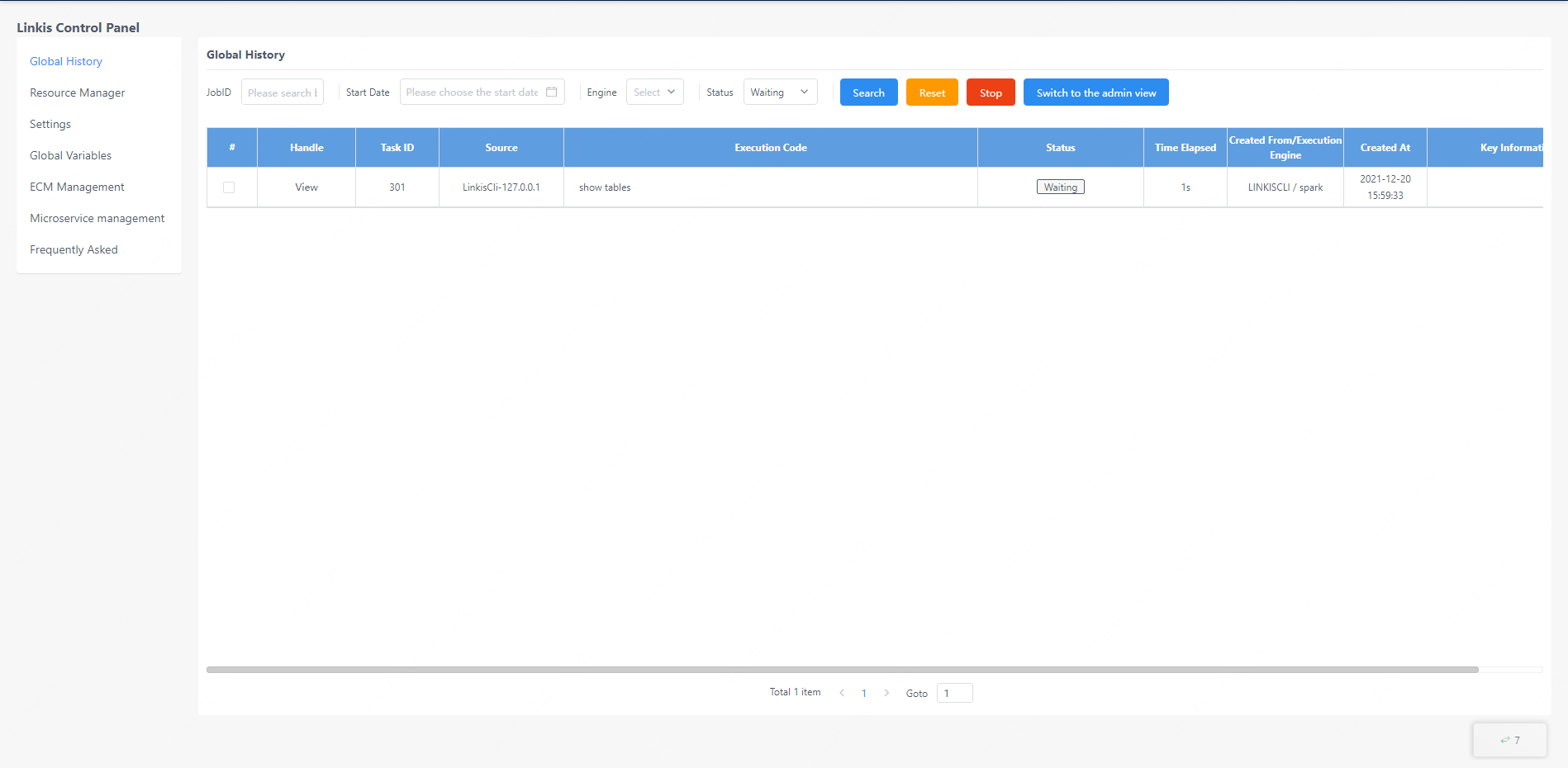
The global history interface provides the user's own linkis task submission record. The execution status of each task can be displayed here, and the reason for the failure of task execution can also be queried by clicking the view button on the left side of the task
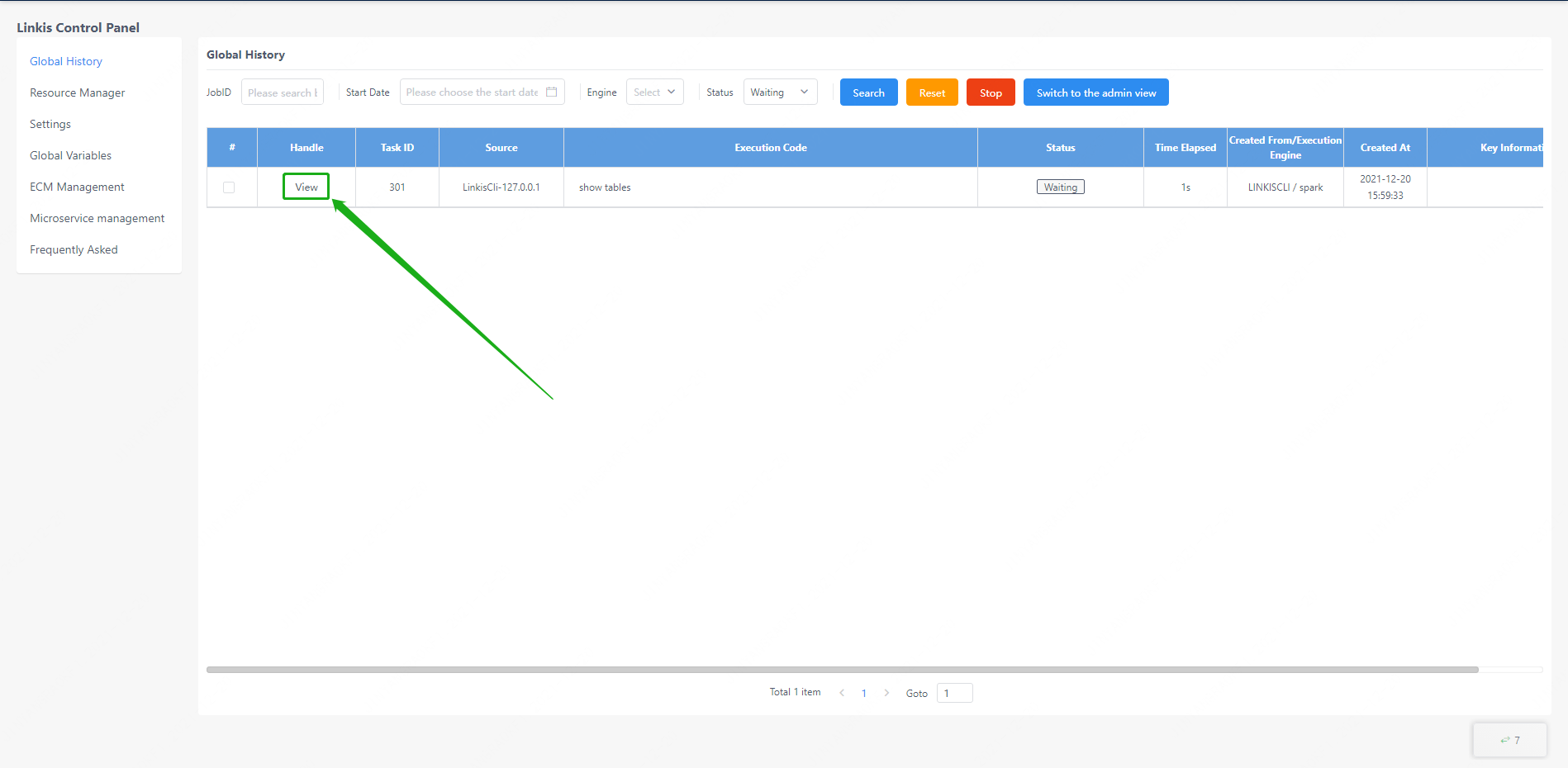
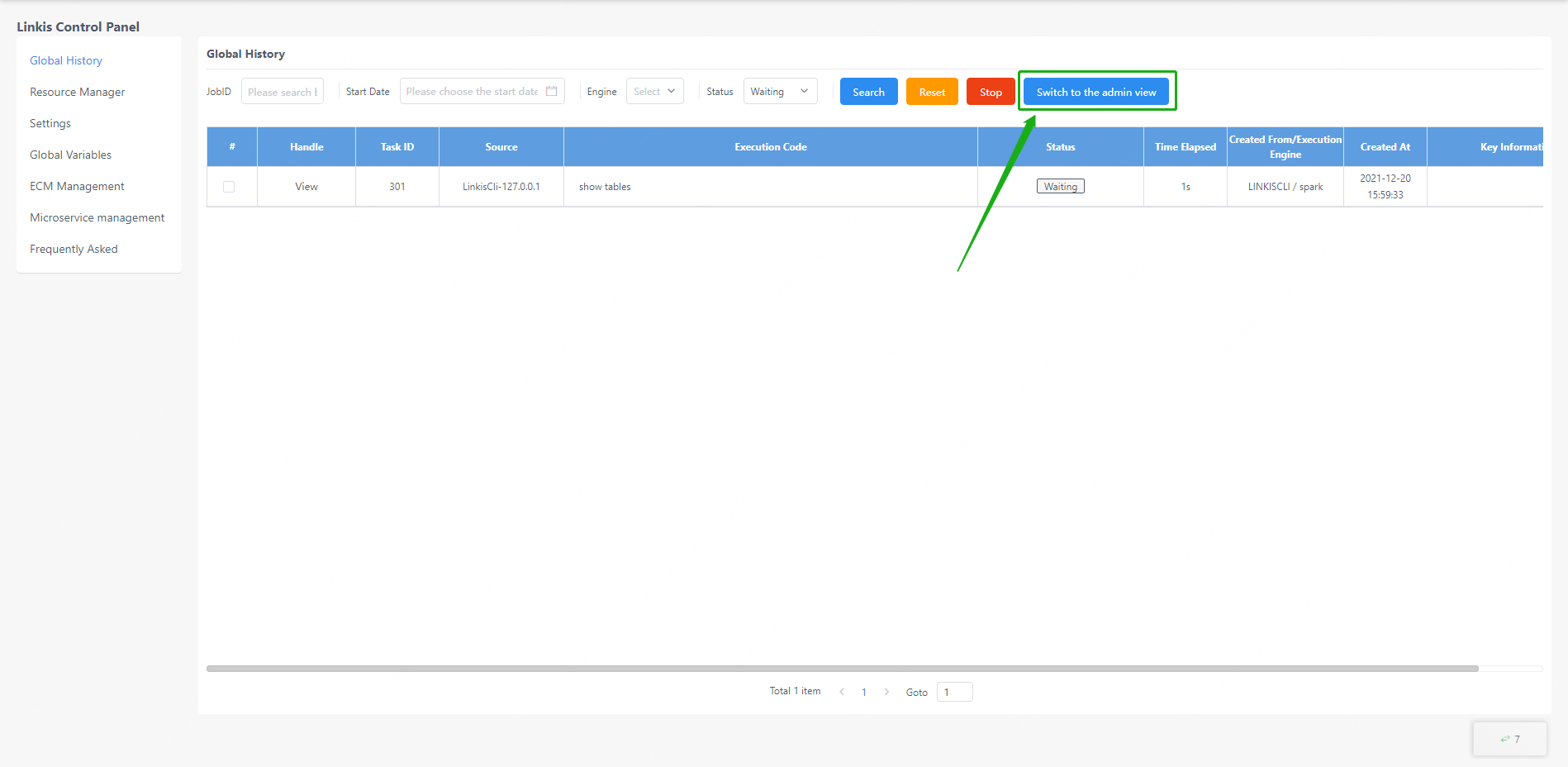
For linkis computing management console administrators, the administrator can view the historical tasks of all users by clicking the switch administrator view on the page.
3. Resource management
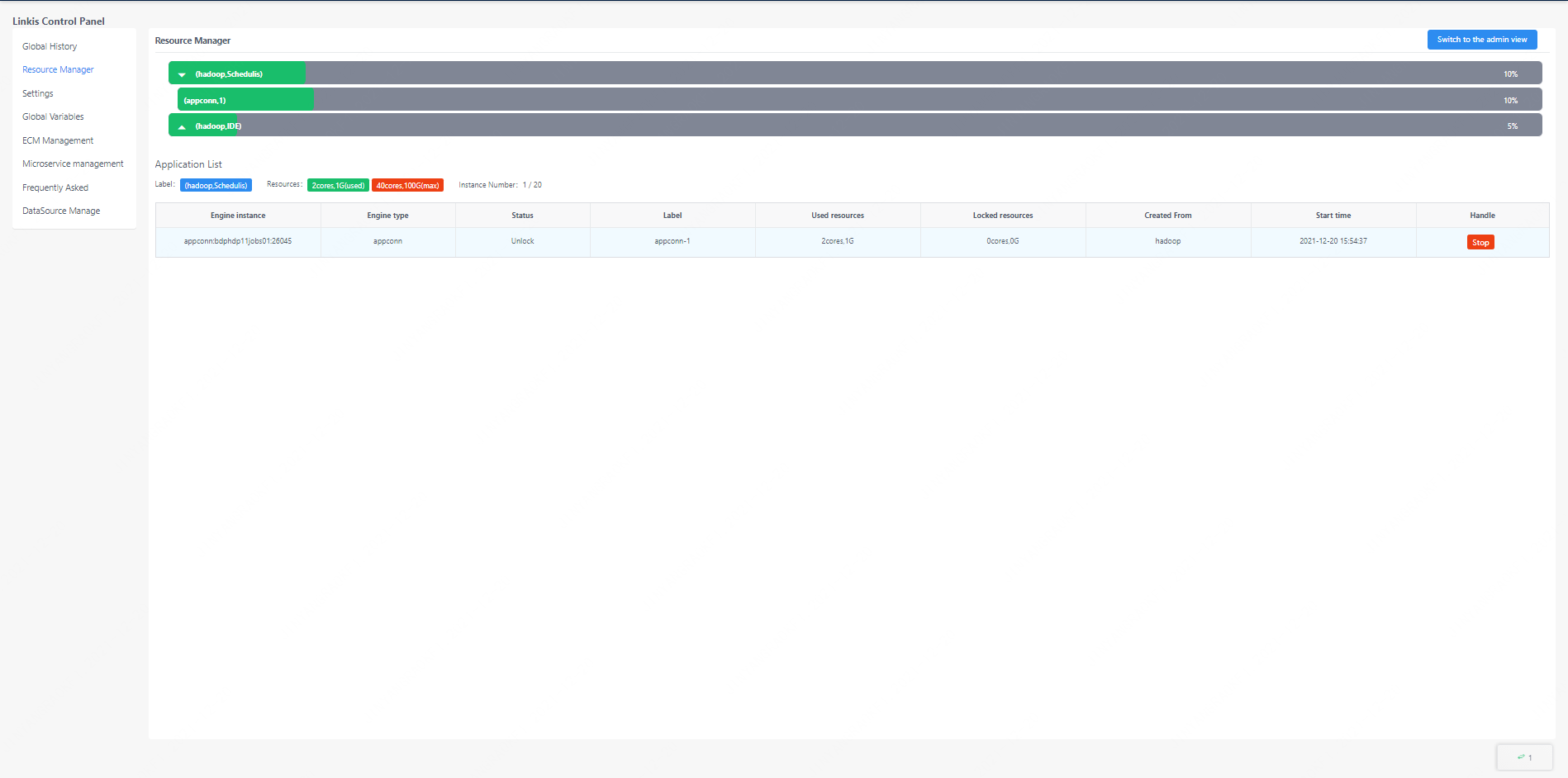
In the resource management interface, the user can see the status of the engine currently started and the status of resource occupation, and can also stop the engine through the page.
4. Parameter configuration
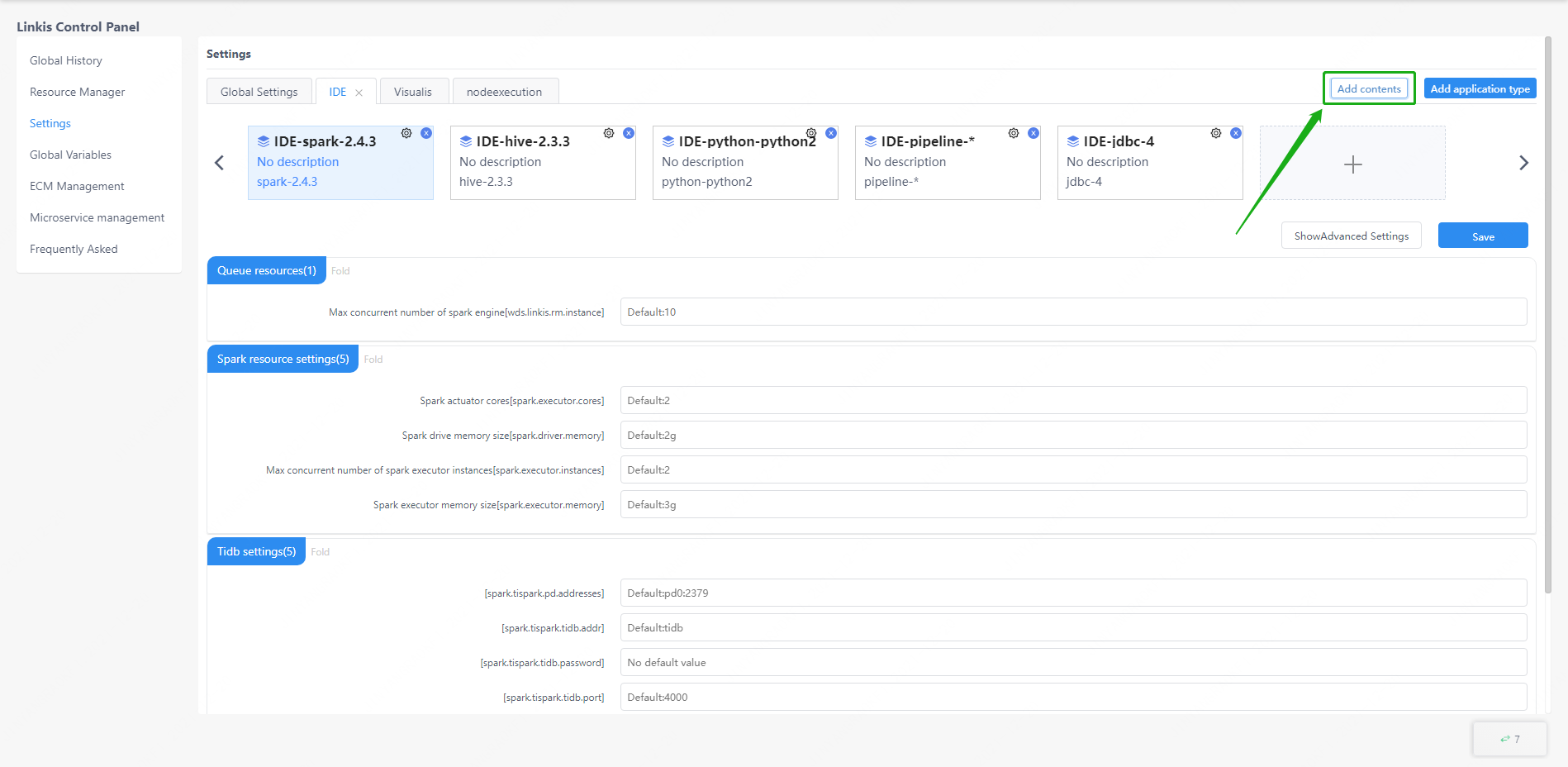
The parameter configuration interface provides the function of user-defined parameter management. The user can manage the related configuration of the engine in this interface, and the administrator can add application types and engines here.
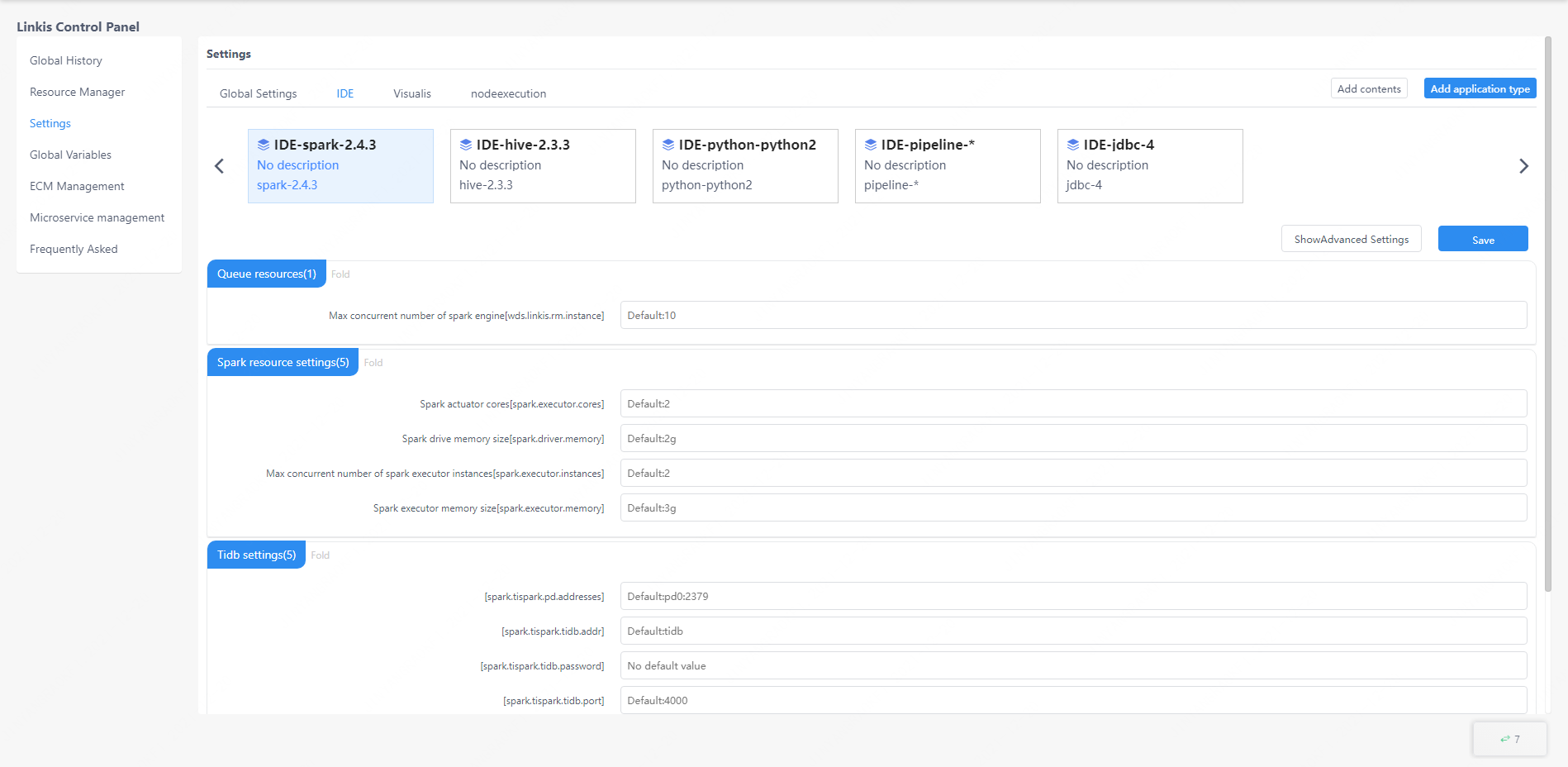
The user can expand all the configuration information in the directory by clicking on the application type at the top and then select the engine type in the application, modify the configuration information and click "Save" to take effect.
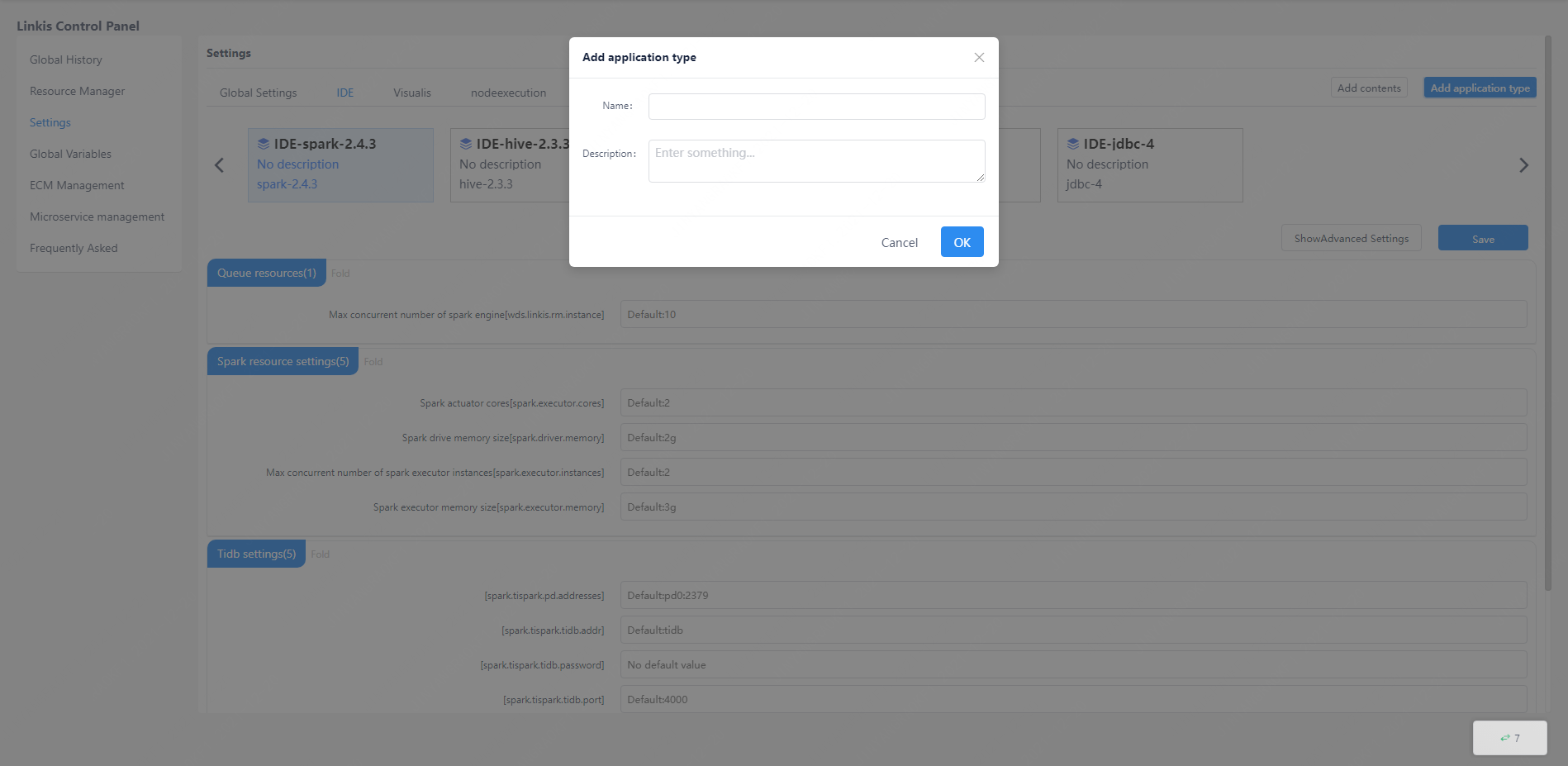
Edit catalog and new application types are only visible to the administrator. Click the edit button to delete the existing application and engine configuration (note! Deleting the application directly will delete all engine configurations under the application and cannot be restored), or add an engine, or click "New Application" to add a new application type.
5. Global variable
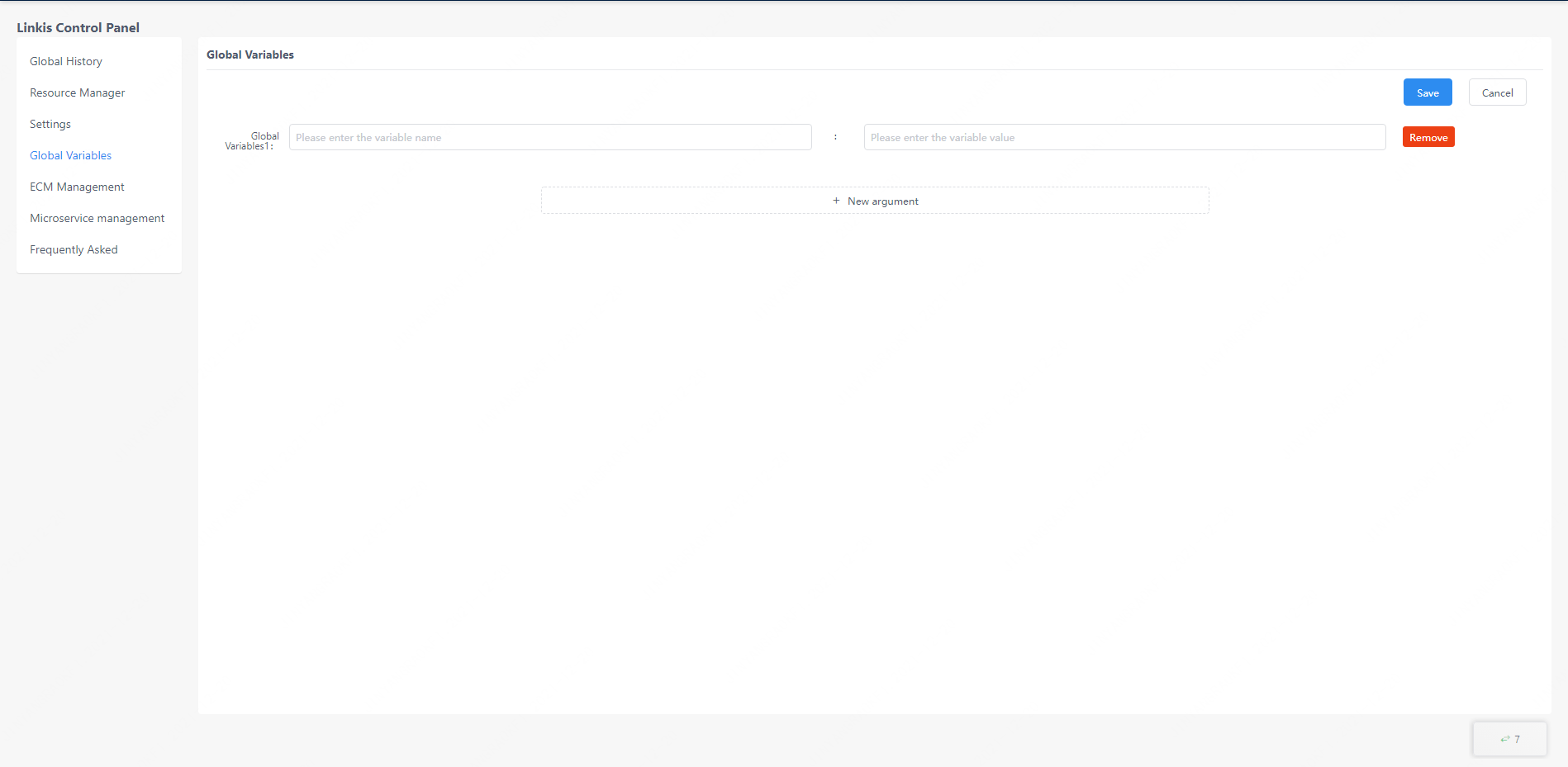
In the global variable interface, users can customize variables for code writing, just click the edit button to add parameters.
6. ECM management
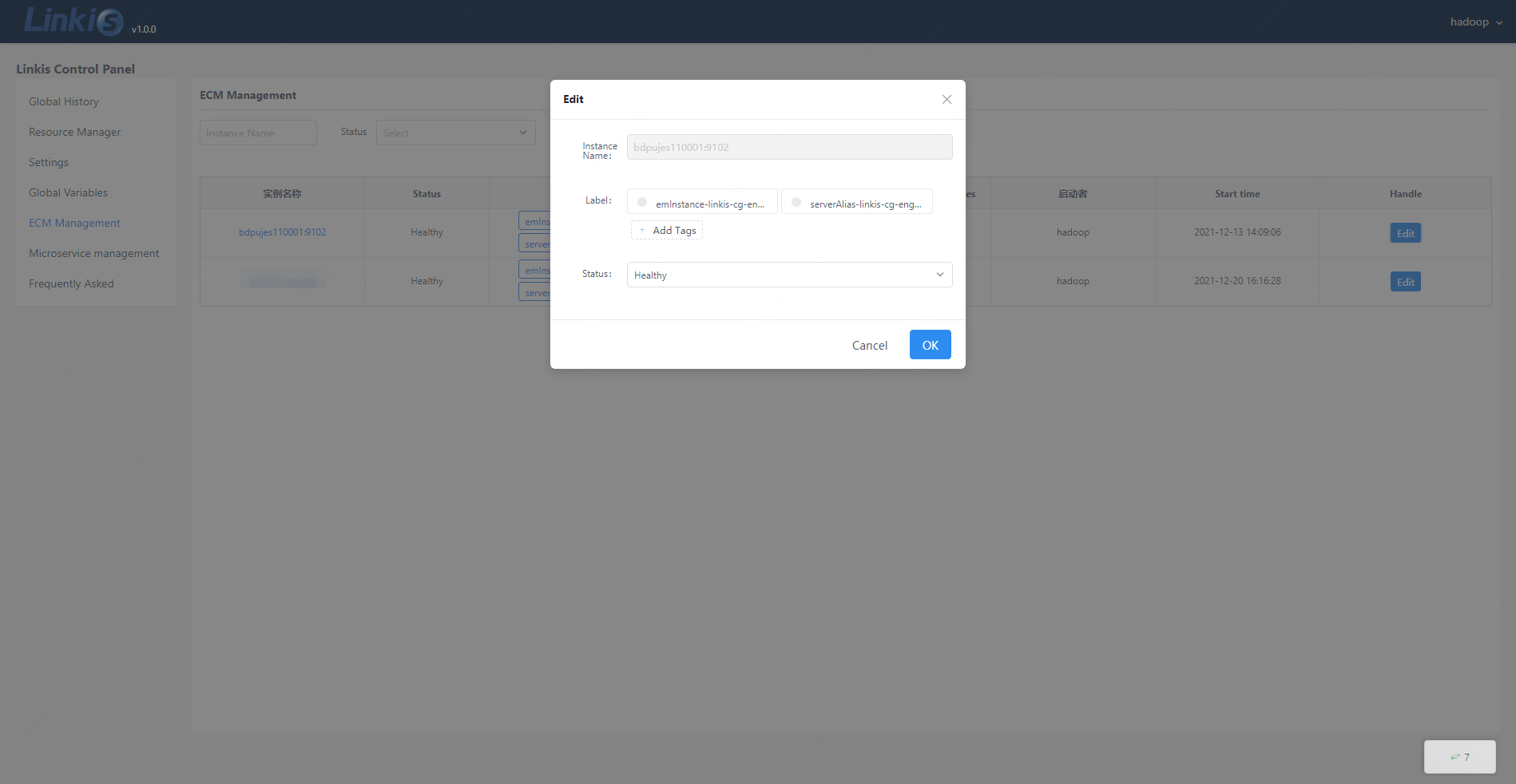
The ECM management interface is used by the administrator to manage the ECM and all engines. This interface can view the status information of the ECM, modify the ECM label information, modify the ECM status information, and query all engine information under each ECM. And only the administrator can see, the administrator's configuration method can be viewed in the second chapter of this article.
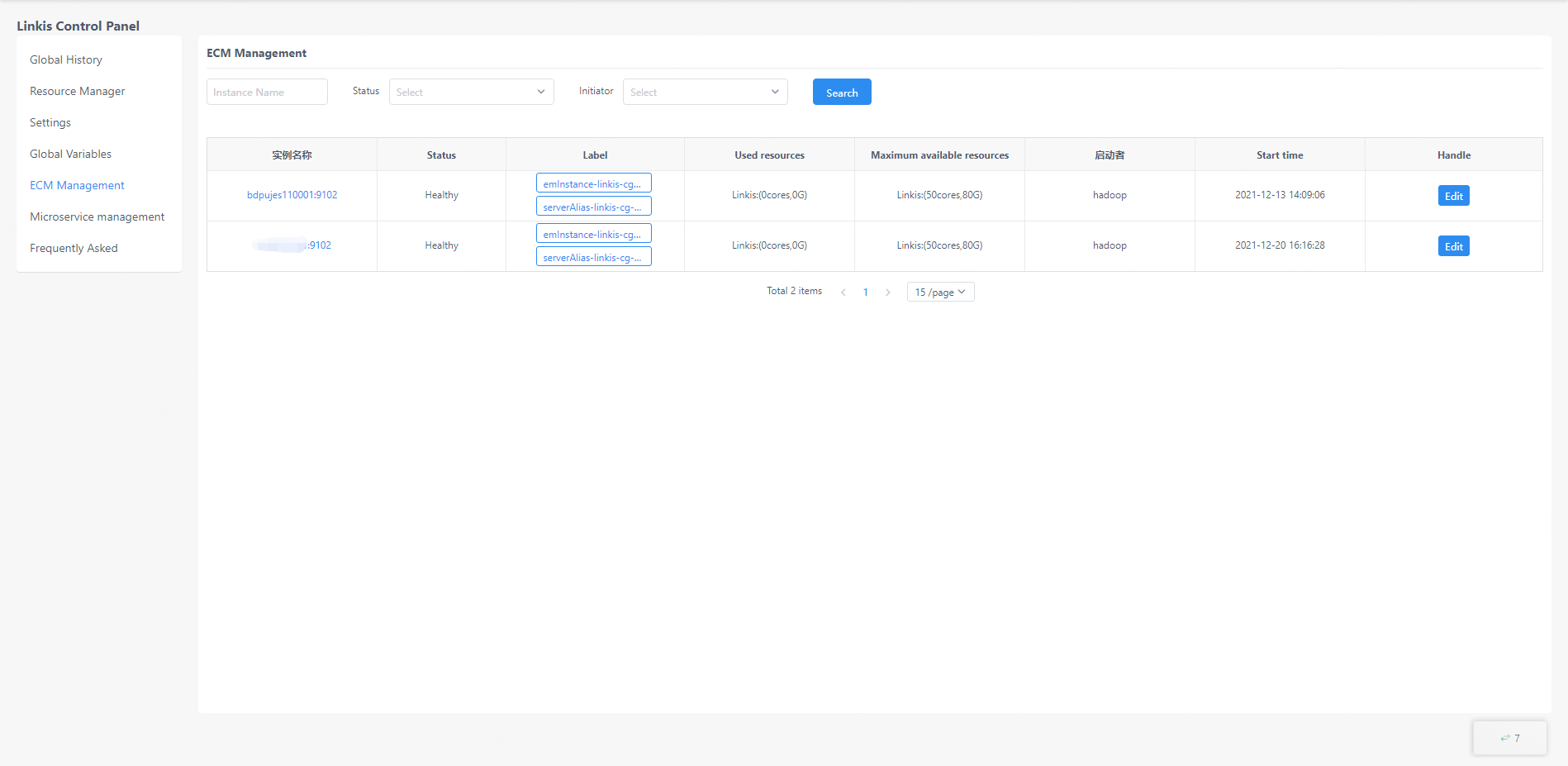
Click the edit button to edit the label information of the ECM (only part of the labels are allowed to be edited) and modify the status of the ECM.
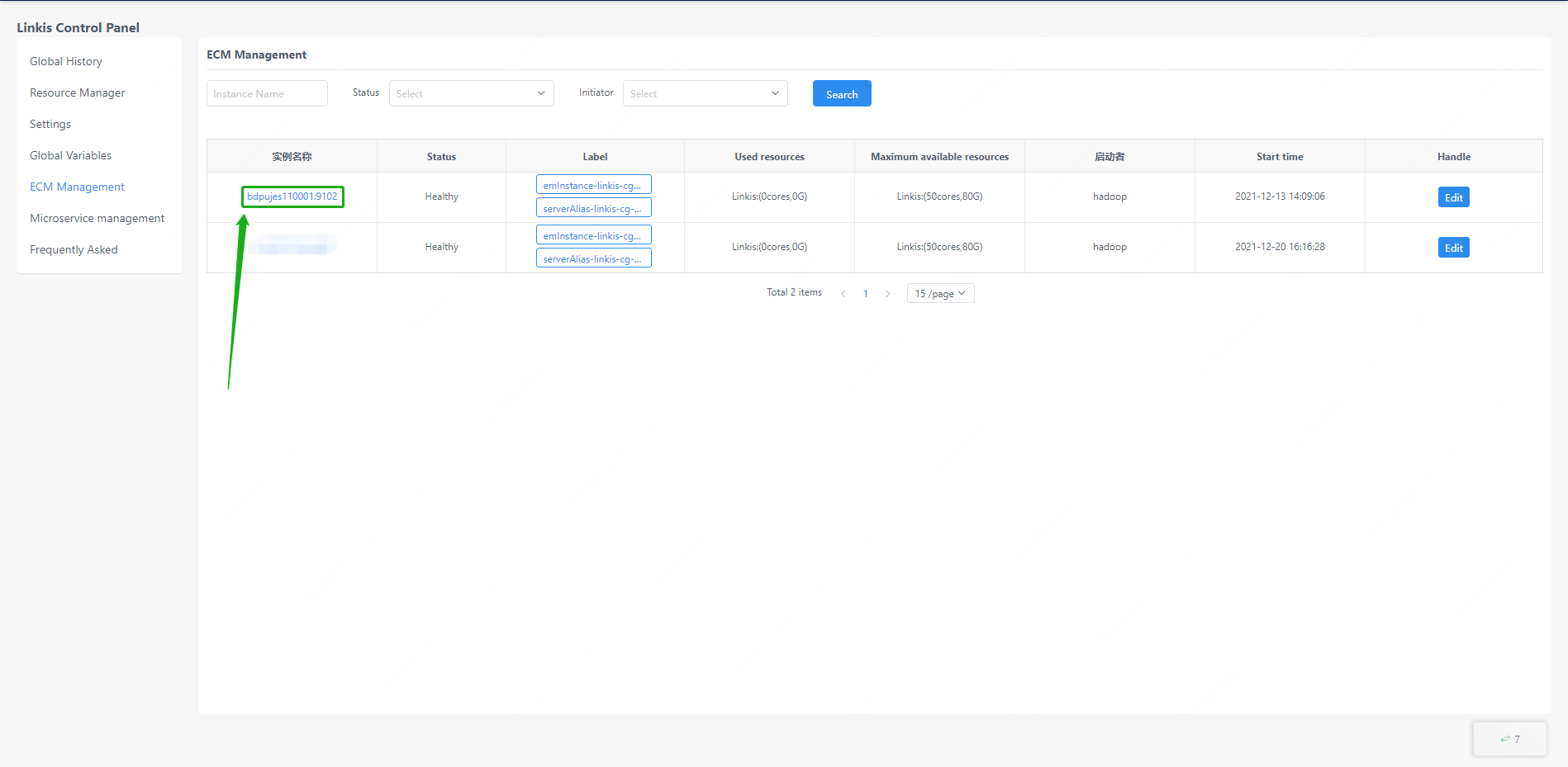
Click the instance name of the ECM to view all engine information under the ECM.
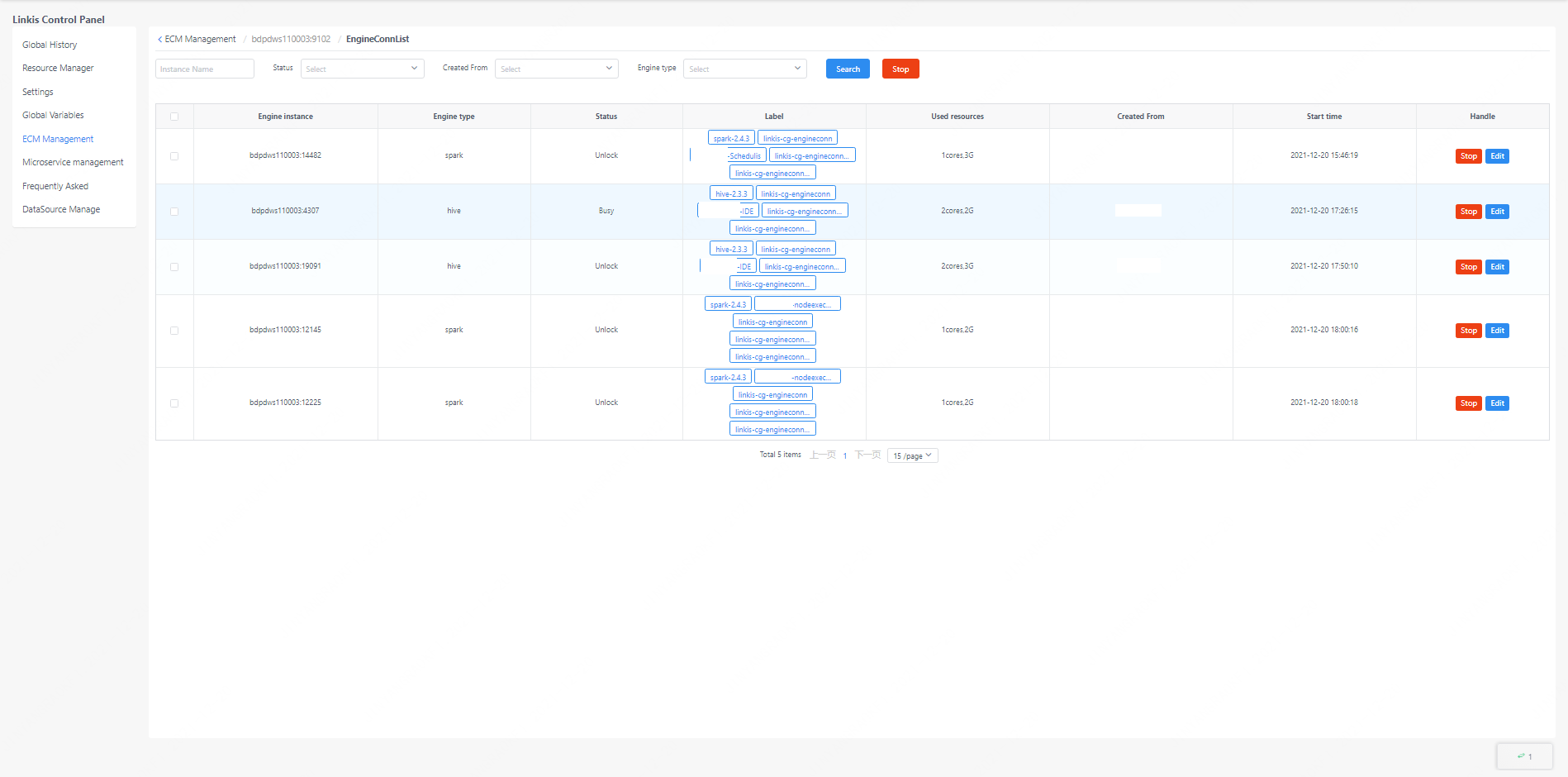
Similarly, you can stop the engine on this interface, and edit the label information of the engine.
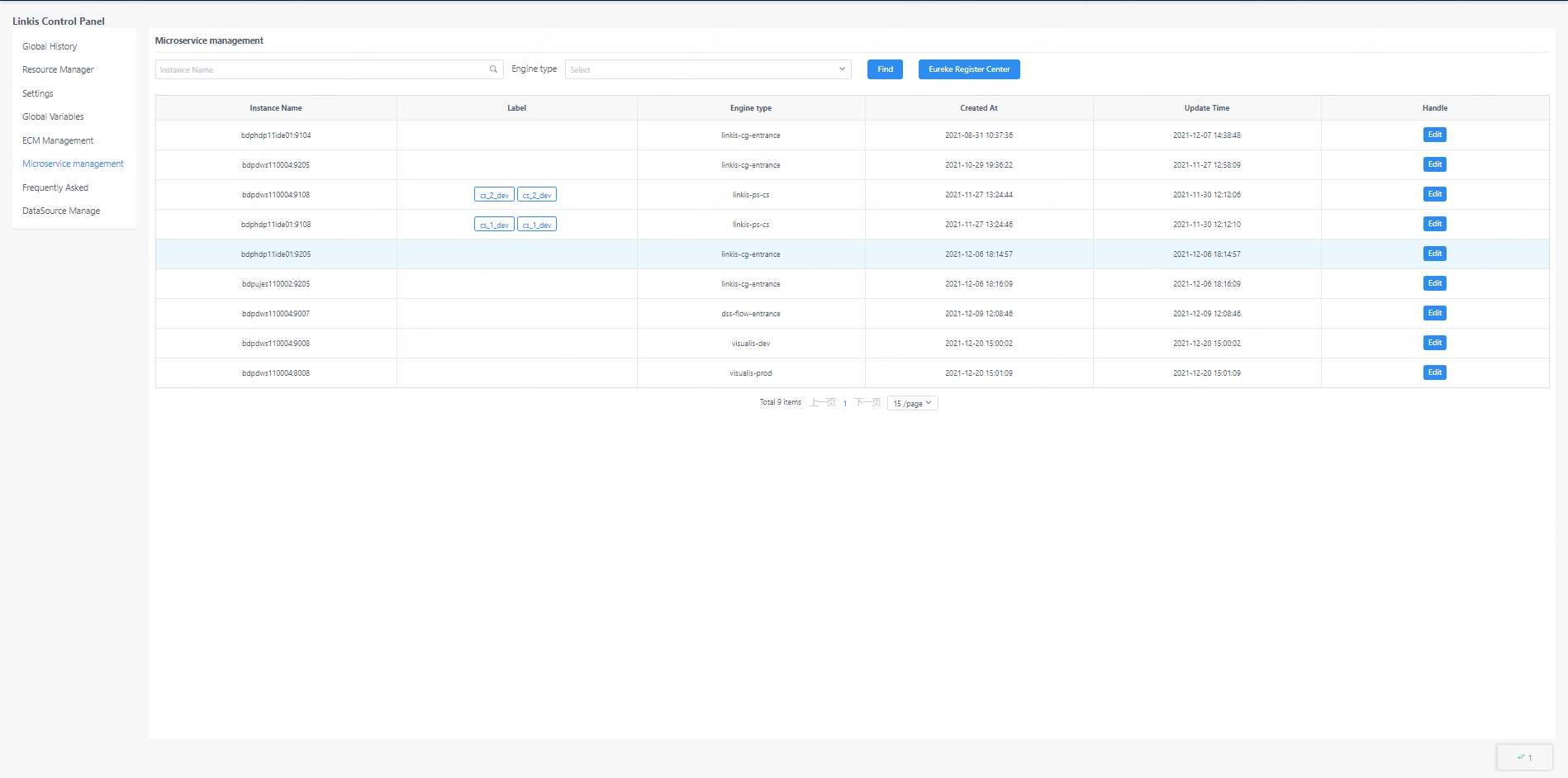
7. Microservice management
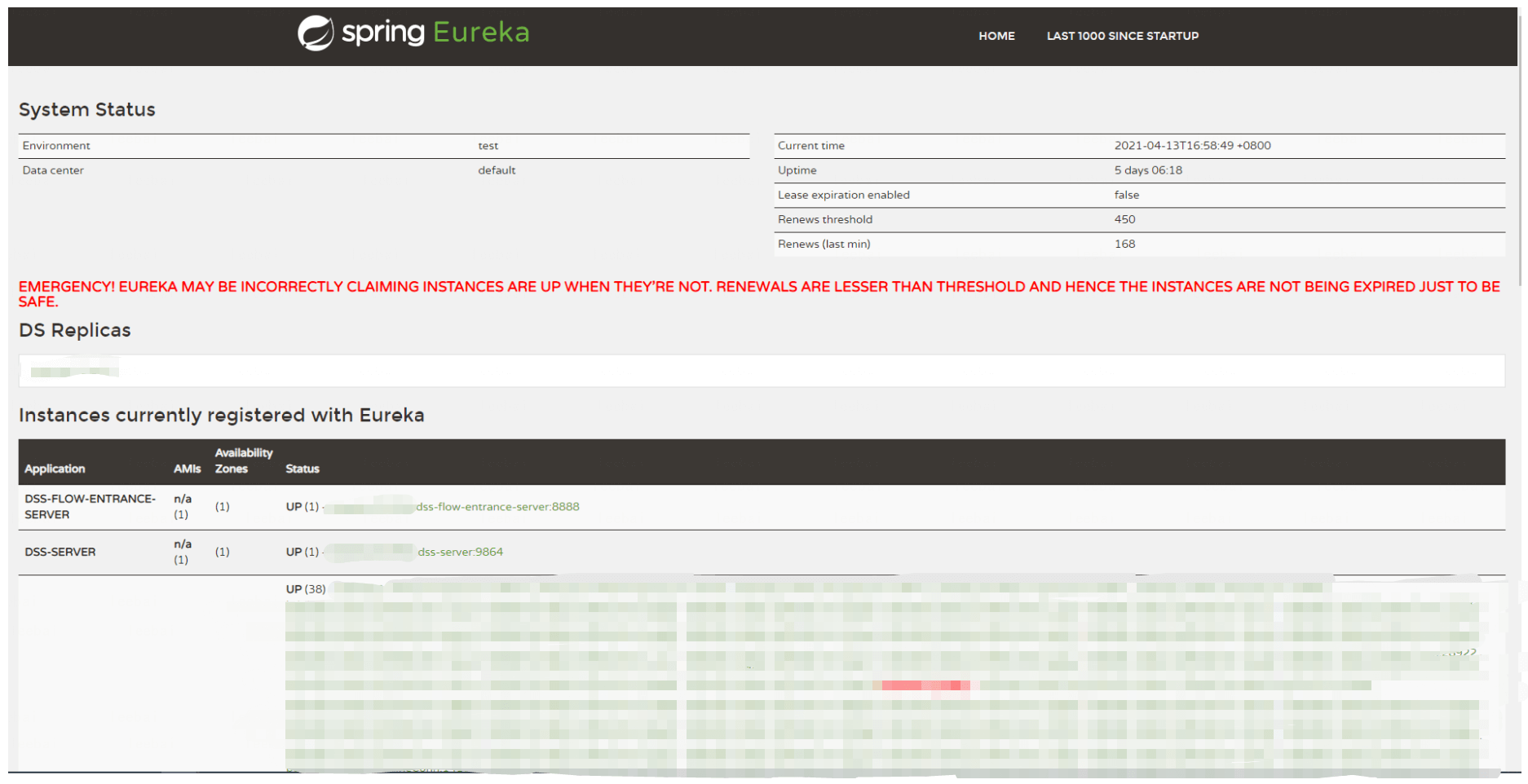
The microservice management interface can view all microservice information under Linkis, and this interface is only visible to the administrator. Linkis's own microservices can be viewed by clicking on the Eureka registration center. The microservices associated with linkis will be listed directly on this interface.