EngineConn Design
1. Overview
EngineConn: engine connector, which is used to connect to the underlying computing and storage engine to complete task execution, task information push and result return, etc. It is the basis for Linkis to provide computing and storage capabilities.
2. Overall Design
The overall design idea of EngineConn is to complete the acquisition and storage of the session information of the underlying engine when starting, complete the connection between the EngineConn process and the underlying engine, and then complete the scheduling of tasks to the underlying engine Session stored in EngineConn through the Executor unit for execution. and get execution-related information.
2.1 Technical Architecture
Introduction to related terms:
EngineConn: Used to store the session information of the underlying engine. To complete the connection with the underlying engine, for example, the Spark engine stores the SparkSession.
Executor: The scheduling executor used to accept the task passed by the caller (such as: Entrance), and finally submit the task to the underlying engine Session for execution. Different tasks implement different Executor classes. The most used is the interactive ComputationExecutor, which is used to accept tasks and push task information to the caller in real time. And the non-interactive ManageableOnceExecutor that accepts only one task is used to complete the submission and execution of the task started by EngineConn.
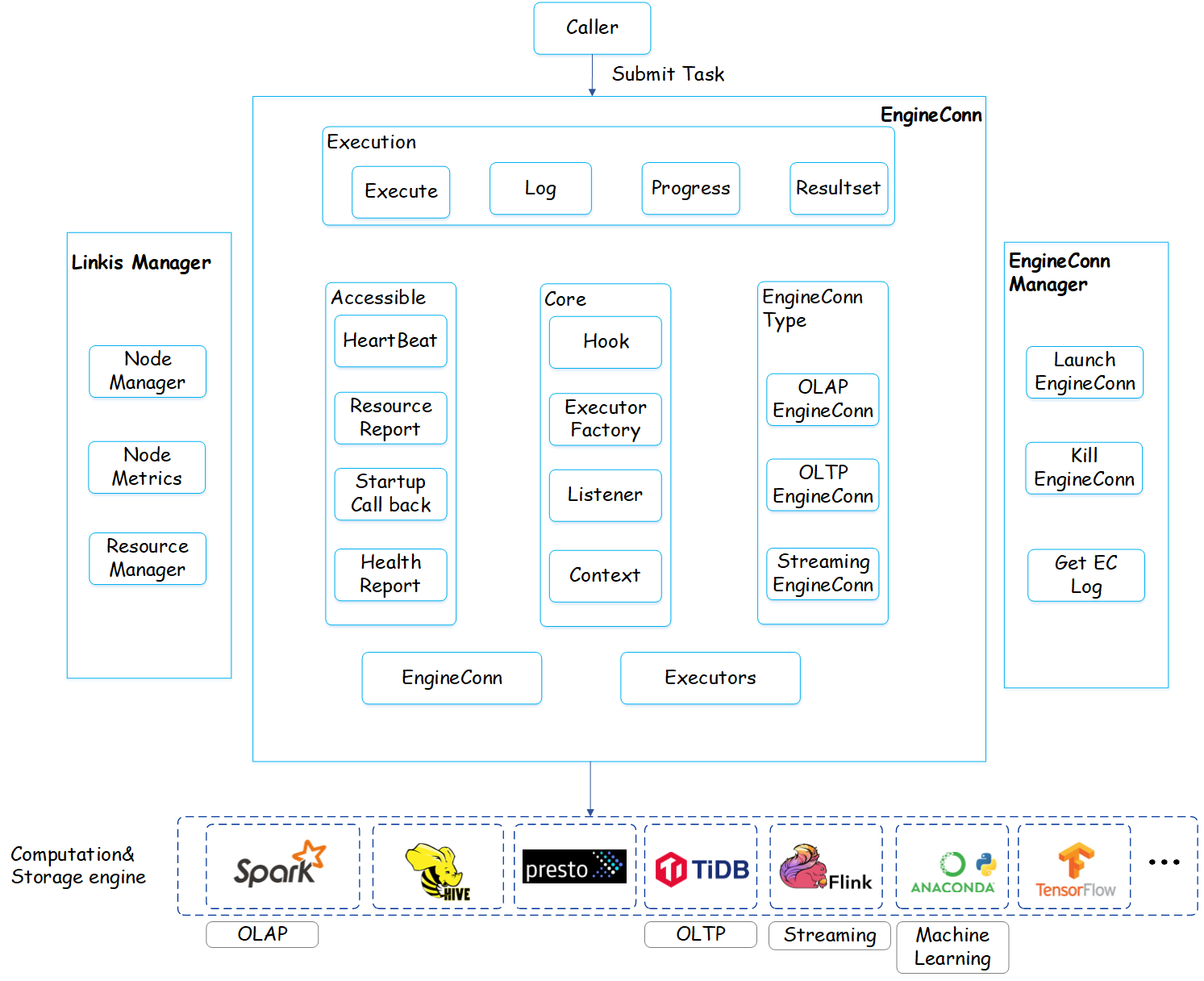
2.2 Business Architecture
| Component name | First-level module | Second-level module | Function points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linkis | EngineConn | linkis-engineconn-common | The common module of engine conn, which defines the most basic entity classes and interfaces in engine conn. |
| Linkis | EngineConn | linkis-engineconn-core | The core module of the engine connector, which defines the interfaces involved in the core logic of EngineConn. |
| Linkis | EngineConn | linkis-executor-core | The core module of the executor, which defines the core classes related to the executor. |
| Linkis | EngineConn | linkis-accessible-executor | The underlying abstraction of the accessible Executor. You can interact with it through RPC requests to obtain its status, load, concurrency and other basic indicators Metrics data |
| Linkis | EngineConn | linkis-computation-engineconn | Related classes that provide capabilities for interactive computing tasks. |
3. Module design
Input: The caller executes the task
Output: return task information such as execution status, results, logs, etc.
Key logic: the timing diagram of the key logic of task execution
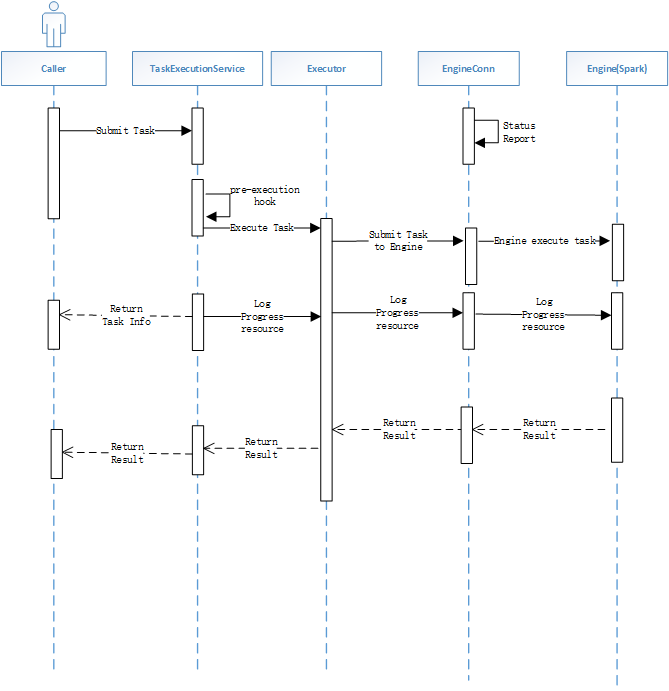
Key Notes:
- If it is a serial Executor, after EngineConn receives a task, it will mark EngineConn as Busy and cannot accept other tasks, and will judge whether the lock of the task is consistent to prevent EngineConn from being submitted by multiple callers at the same time. After the task is executed, it becomes the Unlock state
- If it is a parallel Executor, after EngineConn receives the task, the state is still in the Unlock state, and it can continue to accept the task. Only when the number of concurrent tasks is reached or the machine index is abnormal will it be marked as Busy state
- If it is an Once type task, EngineConn will automatically execute the task after it is started, and the EngineConn process will exit after the task is executed.
4. Data structure/storage design
not involving
5. Interface design
Brief introduction of other classes:
The common module of linkis-engineconn-common engine connector defines the most basic entity classes and interfaces in the engine connector.
| Core Service | Core Function |
|---|---|
| EngineCreationContext | contains the context information of EngineConn during startup |
| EngineConn | contains the specific information of EngineConn, such as type, specific connection information with layer computing storage engine, etc. |
| EngineExecution | Provides the creation logic of Executor |
| EngineConnHook | Defines the operations before and after each stage of engine startup |
The core module of linkis-engineconn-core engine connector defines the interfaces involved in the core logic of EngineConn.
| Core Classes | Core Functions |
|---|---|
| EngineConnManager | Provides related interfaces for creating and obtaining EngineConn |
| ExecutorManager | Provides related interfaces for creating and obtaining Executor |
| ShutdownHook | Defines actions during engine shutdown |
| EngineConnServer | Startup class of EngineConn microservice |
linkis-executor-core is the core module of the executor, which defines the core classes related to the executor. The executor is the real computing execution unit, which is responsible for submitting user code to EngineConn for execution.
| Core Classes | Core Functions |
|---|---|
| Executor | is the actual computing logic execution unit, and provides top-level abstraction of various capabilities of the engine. |
| EngineConnAsyncEvent | defines EngineConn related asynchronous events |
| EngineConnSyncEvent | defines the synchronization event related to EngineConn |
| EngineConnAsyncListener | defines EngineConn-related asynchronous event listeners |
| EngineConnSyncListener | defines EngineConn-related synchronization event listeners |
| EngineConnAsyncListenerBus | Defines the listener bus for EngineConn asynchronous events |
| EngineConnSyncListenerBus | Defines the listener bus for EngineConn sync events |
| ExecutorListenerBusContext | defines the context of the EngineConn event listener |
| LabelService | Provide label reporting function |
| ManagerService | Provides the function of information transfer with LinkisManager |
linkis-accessible-executor: The underlying abstraction of the Executor that can be accessed. You can interact with it through RPC requests to obtain basic metrics such as its status, load, and concurrency.
| Core Classes | Core Functions |
|---|---|
| LogCache | Provides the function of log caching |
| AccessibleExecutor | An Executor that can be accessed and interacted with via RPC requests. |
| NodeHealthyInfoManager | Manage Executor's health information |
| NodeHeartbeatMsgManager | Manage Executor's heartbeat information |
| NodeOverLoadInfoManager | Manage Executor load information |
| Listener-related | Provides events related to Executor and corresponding listener definitions |
| EngineConnTimedLock | Define Executor level lock |
| AccessibleService | Provide the start-stop and status acquisition functions of Executor |
| ExecutorHeartbeatService | Provides Executor's heartbeat-related functions |
| LockService | Provides lock management functions |
| LogService | Provides log management functions |
| EngineConnCallback | Define the callback logic of EngineConn |
Related classes that provide capabilities for interactive computing tasks.
| Core Classes | Core Functions |
|---|---|
| EngineConnTask | defines interactive computing tasks submitted to EngineConn |
| ComputationExecutor | defines an interactive Executor, which has interactive capabilities such as status query and task kill, and can only execute tasks once by default. |
| ConcurrentComputationExecutor | Interactive synchronous concurrent Executor, inherited from ComputationExecutor, but supports executing multiple tasks at the same time |
| AsyncConcurrentComputationExecutor | Interactive asynchronous concurrent Executor, inherited from ComputationExecutor, supports multiple tasks to be executed at the same time, and the task does not occupy the execution thread and adopts the form of asynchronous notification |
| TaskExecutionService | Provides management functions for interactive computing tasks |
6. Non-functional design
6.1 Security
- All the relevant information of the task can only be queried by submitting the user
- The default startup user of the EngineConn process is the submission user
6.2 Performance
EngineConn that supports concurrency supports colleagues to run a large number of tasks concurrently. For example, a single Trino EngineConn can run more than 300 trino tasks at the same time
6.3 Capacity
not involving
6.4 High Availability
EngineConn is a process started on demand and task. Support high availability
6.5 Data Quality
not involving